EV Purchase Intentions Fall Among Canadian Consumers For Third Year
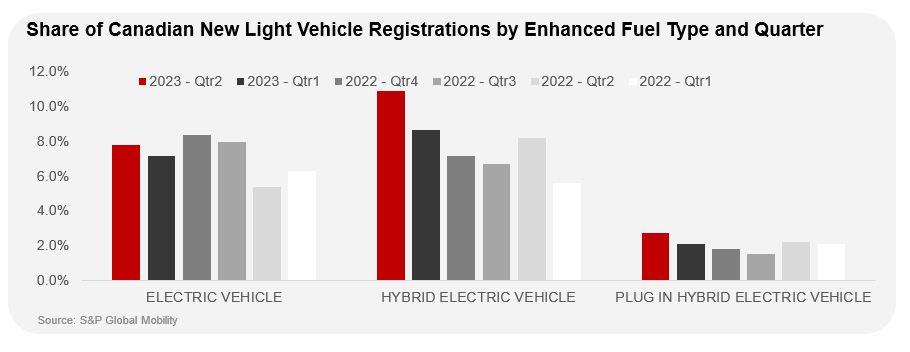
Table of Contents
Rising Costs and Inflation Impacting EV Affordability
The escalating cost of living and persistent inflation are significantly impacting the affordability of EVs in Canada. The price difference between electric vehicles and their gasoline-powered counterparts remains a considerable barrier for many potential buyers.
Increased Vehicle Prices
EV prices have increased substantially in recent years, outpacing the inflation rate for gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Comparison: A mid-size sedan EV might cost $10,000-$20,000 more than a comparable gasoline model. SUVs and trucks see even larger price discrepancies.
- Government Incentives: While government incentives like federal and provincial rebates exist, they often fail to fully offset the higher initial purchase price, leaving many consumers still facing a significant financial burden. The eligibility criteria for these rebates can also be complex and confusing.
- Keywords: EV price increase, inflation, affordability, electric vehicle cost, gasoline car prices.
Battery Costs and Supply Chain Issues
A major driver of high EV prices is the cost of batteries. The complex manufacturing process and reliance on specific raw materials like lithium and cobalt contribute to this cost.
- Raw Material Prices: Fluctuations in lithium and cobalt prices, exacerbated by geopolitical factors and supply chain bottlenecks, directly impact battery production costs and, consequently, the overall price of EVs.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain issues further complicate the situation, leading to production delays and increased manufacturing costs. The ongoing semiconductor chip shortage also affects EV production.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and development efforts focus on improving battery technology, aiming to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Solid-state batteries and other innovations hold the potential to revolutionize the EV market in the future.
- Keywords: lithium prices, cobalt prices, supply chain disruption, battery production cost, EV battery technology.
Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure Concerns
Range anxiety – the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station – remains a significant obstacle to wider EV adoption in Canada. This concern is amplified by shortcomings in the charging infrastructure, particularly outside urban areas.
Limited Driving Range
While EV range is constantly improving, many models still offer a limited driving range compared to gasoline vehicles.
- Range Variations: The range varies greatly among EV models, with some offering over 500 km on a single charge, while others fall considerably short. Weather conditions, driving style, and terrain also impact the actual range achieved.
- Rural Concerns: The limited range is a significant problem in rural areas with sparse charging infrastructure. Long journeys become challenging, potentially causing range anxiety to outweigh the benefits of EV ownership.
- Keywords: EV range anxiety, electric vehicle range, charging infrastructure, fast charging stations, slow charging.
Inadequate Charging Network
Canada’s charging network, while expanding, still falls short of what is needed for widespread EV adoption.
- Charging Station Density: The density of public charging stations varies significantly across the country, with major urban centers having far more access than rural communities. This disparity creates an uneven playing field for potential EV buyers.
- Charging Infrastructure Challenges: Installing and maintaining a robust and reliable charging network requires significant investment, coordination between government, private sector, and utilities. Finding suitable locations, obtaining necessary permits, and ensuring grid capacity are some of the hurdles to overcome.
- Home Charging: While home charging is a solution for many, it's not feasible for apartment dwellers or those without access to dedicated parking.
- Keywords: charging station density, EV charging network, public charging stations, home charging, fast charging network.
Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives play a crucial role in stimulating EV adoption, but their effectiveness requires careful consideration.
Impact of Federal and Provincial Incentives
Canada offers various federal and provincial incentives, including tax credits and rebates, aimed at making EVs more affordable. However, their impact is not uniform.
- Incentive Types: The specifics of incentives vary across provinces, potentially leading to confusion and inequality among potential buyers.
- Accessibility: The complexity of application processes and eligibility criteria can hinder accessibility. Many consumers might be unaware of the available incentives or find the process too cumbersome.
- Effectiveness: While incentives help, they are often insufficient to fully overcome the price barrier, especially for lower-income consumers. More comprehensive and accessible incentives might be needed.
- Keywords: EV incentives, government subsidies, tax credits, rebates, electric vehicle policy, clean energy policy.
Lack of Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education initiatives regarding EV benefits are essential to drive adoption.
- Misconceptions: Many potential buyers harbor misconceptions about EV technology, range, charging times, and maintenance. Effective public awareness campaigns need to address these misconceptions.
- Benefits Communication: Campaigns should effectively communicate the environmental benefits, long-term cost savings (reduced fuel and maintenance), and technological advancements in EV technology.
- Keywords: EV education, consumer awareness, public awareness campaign, EV benefits, environmental benefits.
Conclusion
The decline in EV purchase intentions among Canadian consumers reflects a complex interplay of factors: rising prices due to inflation and supply chain issues, range anxiety fueled by limited driving range and insufficient charging infrastructure, and the imperfect effectiveness of government incentives and public awareness campaigns. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach, including more substantial and accessible incentives, further investment in charging infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, and targeted public awareness campaigns aimed at dispelling misconceptions and highlighting the overall benefits of EV ownership. Understanding the factors influencing EV purchase intentions is crucial. Stay informed about the latest developments in electric vehicle technology, government incentives, and charging infrastructure to make an informed decision about your next vehicle purchase. Continue to follow our coverage on EV purchase intentions in Canada for the latest updates.

Featured Posts
-
 The Importance Of Middle Managers Benefits For Companies And Employees
Apr 27, 2025
The Importance Of Middle Managers Benefits For Companies And Employees
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Movies And Shows To Watch On Kanopy A Free Streaming Guide
Apr 27, 2025
Movies And Shows To Watch On Kanopy A Free Streaming Guide
Apr 27, 2025 -
 David Geiers Vaccine Review Hhs Under Fire For Controversial Appointment
Apr 27, 2025
David Geiers Vaccine Review Hhs Under Fire For Controversial Appointment
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Mc Cook Jeweler Provides Support To Nfl Players Seeking A Second Chance
Apr 27, 2025
Mc Cook Jeweler Provides Support To Nfl Players Seeking A Second Chance
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Trump Predicts Trade Deal Conclusion In 3 4 Weeks
Apr 27, 2025
Trump Predicts Trade Deal Conclusion In 3 4 Weeks
Apr 27, 2025
