EU's Strategy: Targeting The Spot Market For Russian Natural Gas Elimination
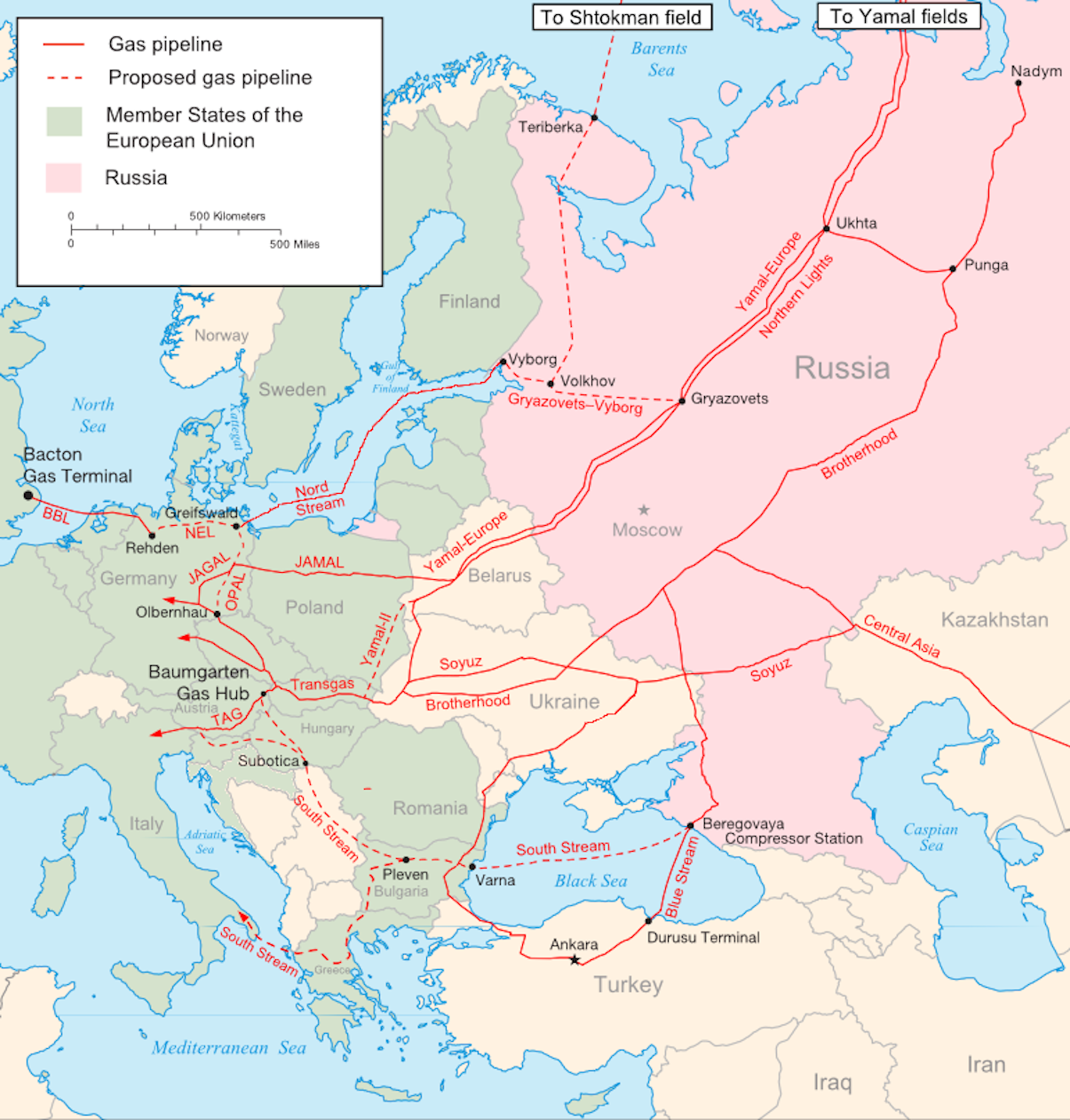
Table of Contents
The Vulnerability of Long-Term Contracts with Russia
The EU's historical reliance on long-term contracts with Russia for natural gas has created significant vulnerabilities. These contracts, often negotiated decades ago, have left the EU exposed to price volatility and unpredictable supply disruptions.
High Prices and Supply Instability
Long-term contracts with Russia, primarily through Gazprom, have consistently demonstrated their limitations. Russia's state-controlled energy giant has leveraged its position to influence prices and, at times, manipulate supply.
- Examples of past supply cuts: The 2006 and 2009 gas crises highlighted the risks of relying on a single major supplier, demonstrating the vulnerability of long-term contracts to geopolitical pressures.
- Price manipulation attempts by Russia: Accusations of price gouging and strategic supply reductions have underscored the need for a more diversified and secure energy supply.
- Impact on EU industries: Supply disruptions have caused significant economic damage to energy-intensive industries across the EU, impacting production and competitiveness.
The consequences of this dependence on Russian energy are clear: long-term contracts have created a dangerous situation of price volatility and supply disruption, ultimately hindering the EU's energy security.
Shifting towards Spot Market Purchases
To mitigate the risks associated with long-term contracts, the EU is actively promoting a shift towards spot market purchases. This transition offers greater flexibility and allows the EU to source gas from a wider range of suppliers.
- Government incentives: The EU is providing financial incentives and support to encourage member states to diversify their energy sources and explore spot market options.
- Diversification of suppliers: The EU is actively seeking to establish relationships with alternative gas suppliers, including countries in North Africa, the Middle East, and the USA.
- Development of gas storage facilities: Significant investment is being made to expand gas storage capacity across the EU, enabling better management of supply fluctuations in the spot market.
- Promotion of LNG imports: The EU is investing heavily in the development of LNG terminal infrastructure, facilitating imports of liquefied natural gas from global suppliers.
By embracing the spot market, the EU aims to increase market flexibility and reduce its dependence on a single, unreliable supplier.
Diversifying Gas Sources to Reduce Reliance on Russia
Diversifying gas sources is a cornerstone of the EU's strategy to eliminate Russian natural gas. This involves both increasing LNG imports and promoting the development of renewable energy sources.
Increased LNG Imports
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is playing a crucial role in the EU's efforts to diversify its gas supply. The construction of new LNG terminals and expansion of existing infrastructure are underway across several member states.
- Construction of new LNG terminals: Significant investments are being made in the development of new LNG import terminals to accommodate increased LNG shipments.
- Expansion of existing infrastructure: Existing LNG terminals are being upgraded and expanded to increase their capacity and efficiency.
- Negotiations with LNG exporting countries: The EU is actively negotiating long-term supply contracts with major LNG exporters like Qatar, the USA, and others.
This increase in LNG imports is a vital step towards reducing the EU's dependence on pipeline gas from Russia.
Promoting Renewable Energy Sources
The EU recognizes that long-term energy security requires a significant shift towards renewable energy sources. The transition to renewables will reduce dependence on fossil fuels and improve energy independence.
- Investment in renewable energy projects: The EU is actively investing in wind, solar, and other renewable energy projects across its member states.
- EU Green Deal initiatives: The EU Green Deal is a comprehensive framework for achieving climate neutrality by 2050, encompassing significant investments in renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- Energy efficiency measures: Improvements in energy efficiency across the EU will reduce overall energy consumption and diminish the reliance on gas imports.
- Support for renewable energy technologies: The EU is providing support and funding for research and development of cutting-edge renewable energy technologies.
The transition to renewable energy is a long-term strategy, but essential for a sustainable and secure energy future for the EU.
Strengthening EU Energy Market Regulations and Cooperation
Strengthening the EU's internal energy market and enhancing strategic gas storage are crucial elements in achieving energy independence.
Strengthening the Internal Energy Market
Improving the efficiency and resilience of the EU's internal energy market is vital for ensuring a secure energy supply for all member states.
- Improved cross-border gas infrastructure: Enhancing gas interconnections between member states will allow for greater flexibility in gas supply and distribution.
- Harmonization of market regulations: Harmonizing energy market rules across the EU will create a more efficient and transparent energy market.
- Joint gas purchasing mechanisms: Joint gas purchasing initiatives can help to leverage greater negotiating power with gas suppliers and secure better prices.
A more integrated and efficient internal energy market is crucial to address future energy security challenges.
Enhancing Strategic Gas Storage
Increased gas storage capacity is essential to mitigate supply disruptions and stabilize gas prices.
- Investment in new storage facilities: The EU is promoting investment in new underground gas storage facilities to increase its overall storage capacity.
- Mandatory filling levels: Regulations are being introduced to ensure that gas storage facilities maintain minimum filling levels throughout the year.
- Coordinated release of gas reserves: Mechanisms for the coordinated release of strategic gas reserves during times of crisis are being established.
Strategic gas storage is a critical tool for enhancing energy security and managing supply volatility.
Conclusion
The EU's strategy to eliminate Russian natural gas, with its focus on the spot market, is a complex and multifaceted undertaking. By actively diversifying gas sources, strengthening energy market regulations, and investing heavily in renewable energies, the EU aims to break free from its dependence on Russian energy supplies and create a more secure and resilient energy future. While challenges remain, the concerted efforts towards reducing reliance on long-term contracts and embracing the flexibility of the spot market are crucial steps in achieving lasting energy independence. Continue to follow developments in the EU's efforts to eliminate Russian natural gas and participate in the discussion on how to further advance this crucial initiative.

Featured Posts
-
 Credit Card Industry Faces Headwinds Amidst Consumer Spending Slowdown
Apr 24, 2025
Credit Card Industry Faces Headwinds Amidst Consumer Spending Slowdown
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Village Roadshows 417 5 Million Alcon Deal Approved Key Details
Apr 24, 2025
Village Roadshows 417 5 Million Alcon Deal Approved Key Details
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Trumps Cuts And The Increased Risk Of Tornadoes This Season
Apr 24, 2025
Trumps Cuts And The Increased Risk Of Tornadoes This Season
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Defamation Claim Against Fox News Allegations And Implications
Apr 24, 2025
Ray Epps Defamation Claim Against Fox News Allegations And Implications
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Trumps Transgender Sports Ban Faces Legal Challenge From Minnesota Ag
Apr 24, 2025
Trumps Transgender Sports Ban Faces Legal Challenge From Minnesota Ag
Apr 24, 2025
