Search Monopoly Lawsuit: Google And The DOJ Head Back To Court

Table of Contents
The DOJ's Case Against Google: Key Allegations
The DOJ's case against Google centers on allegations of anti-competitive practices that have allowed the company to maintain its dominant position in the search engine market. This alleged search monopoly stifles innovation and limits consumer choice, harming both businesses and individuals. The keywords surrounding this section include: Antitrust violations, Search Engine Market Share, Predatory Practices, Google Search, and Market Domination.
-
Exclusive Agreements: The DOJ alleges Google maintains its dominance through exclusive agreements with mobile device manufacturers and internet service providers (ISPs). These agreements often make Google Search the default search engine, hindering the ability of competitors to gain traction. This alleged practice effectively locks in Google's position and creates barriers to entry for rivals.
-
Stifling Innovation: The lawsuit claims Google's overwhelming market share stifles innovation. By controlling such a large portion of the online search market, Google allegedly discourages the development and adoption of alternative search engines and related technologies. This lack of competition potentially harms users by limiting the development of improved search technologies and features.
-
Market Domination Evidence: The DOJ's case will likely present data demonstrating Google’s extraordinarily large market share compared to competitors like Bing or DuckDuckGo. This evidence aims to show the extent of Google’s control and the significant barrier to entry it creates for potential rivals in the search engine market.
-
Specific Examples of Anti-competitive Behavior: The lawsuit will likely highlight specific instances of alleged anti-competitive behavior. This might include evidence of payments made to mobile manufacturers and ISPs to ensure Google Search remains the pre-installed and default option. This, the DOJ argues, is not fair competition.
Google's Defense Strategy and Counterarguments
Google's defense will likely focus on arguing that its market dominance is a result of providing superior products and services that have earned consumer trust. Key terms for this section are: Google Defense, Innovation, Competition, Consumer Benefits, and Free Services.
-
Superior Products and Services: Google will likely argue its large market share is a direct result of offering a superior search experience compared to competitors. They will emphasize the accuracy, speed, and comprehensiveness of their search results.
-
Consumer Benefits: A central part of their defense will highlight the numerous benefits consumers receive from free and readily accessible search results. They will emphasize the value proposition of their search engine and related services.
-
Data-Driven Innovation: Google's defense might also focus on the use of its vast data sets to fuel innovation in multiple areas, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other digital products. This, they argue, benefits both consumers and businesses.
-
Existing Competition: Google will undoubtedly point to the existence of competing search engines, like Bing and DuckDuckGo, as evidence that a competitive landscape exists, although their much smaller market shares are undeniable.
The Role of Mobile Operating Systems in the Lawsuit
A key aspect of the DOJ's case involves Google's agreements with mobile phone manufacturers to pre-install Google Search as the default search engine on Android devices. Keywords here include: Android, Mobile Search, Default Search Engine, Pre-installation, and Market Power.
-
Default Search Engine Pre-installation: The lawsuit will likely heavily scrutinize these pre-installation agreements. The DOJ will argue that this practice artificially inflates Google’s market share and prevents consumers from easily switching to alternative search engines.
-
Maintaining Market Dominance: The DOJ’s claim is that this pre-installation is a crucial tactic in Google's strategy to maintain its overwhelming market share and stifle competition in the mobile search market.
-
Google's Counterarguments: Google's counterarguments will likely emphasize the convenience for users who benefit from having a familiar search engine pre-installed. They might also point to the freedom manufacturers have to choose alternative default search engines if they prefer.
Potential Implications and Outcomes of the Lawsuit
The potential implications and outcomes of this search monopoly lawsuit are far-reaching. The keywords are: Antitrust Remedies, Market Regulation, Breakup, Fines, and Consent Decree.
-
Range of Outcomes: Possible outcomes range from significant financial penalties to structural remedies such as the forced divestiture of certain assets. The judge could mandate changes to Google’s business practices.
-
Changes to Pre-installation Practices: A court order could require Google to alter its practices concerning the pre-installation of search engines on mobile devices, potentially mandating clearer choices for consumers.
-
Impact on Tech Giants: The ruling could significantly impact how tech giants operate in the digital marketplace and potentially set precedents for future antitrust cases involving other major tech companies.
-
Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: The case could usher in a new era of increased regulatory scrutiny of major tech companies, particularly concerning their market power and potential anti-competitive behaviors.
Conclusion
The ongoing search monopoly lawsuit against Google represents a pivotal moment in the ongoing debate surrounding antitrust law and the power of tech giants. The outcome will have significant consequences for the competitive landscape of online search and could set a precedent for future regulatory actions concerning digital monopolies. Staying informed about the developments in this crucial search monopoly lawsuit is essential. Understanding the complexities of this case is critical to navigating the ever-evolving landscape of online competition and search engine market dynamics. Follow reputable news sources to keep abreast of the latest updates in this significant Google lawsuit.

Featured Posts
-
 Stock Market Pain Investors Brace For Further Losses
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Pain Investors Brace For Further Losses
Apr 22, 2025 -
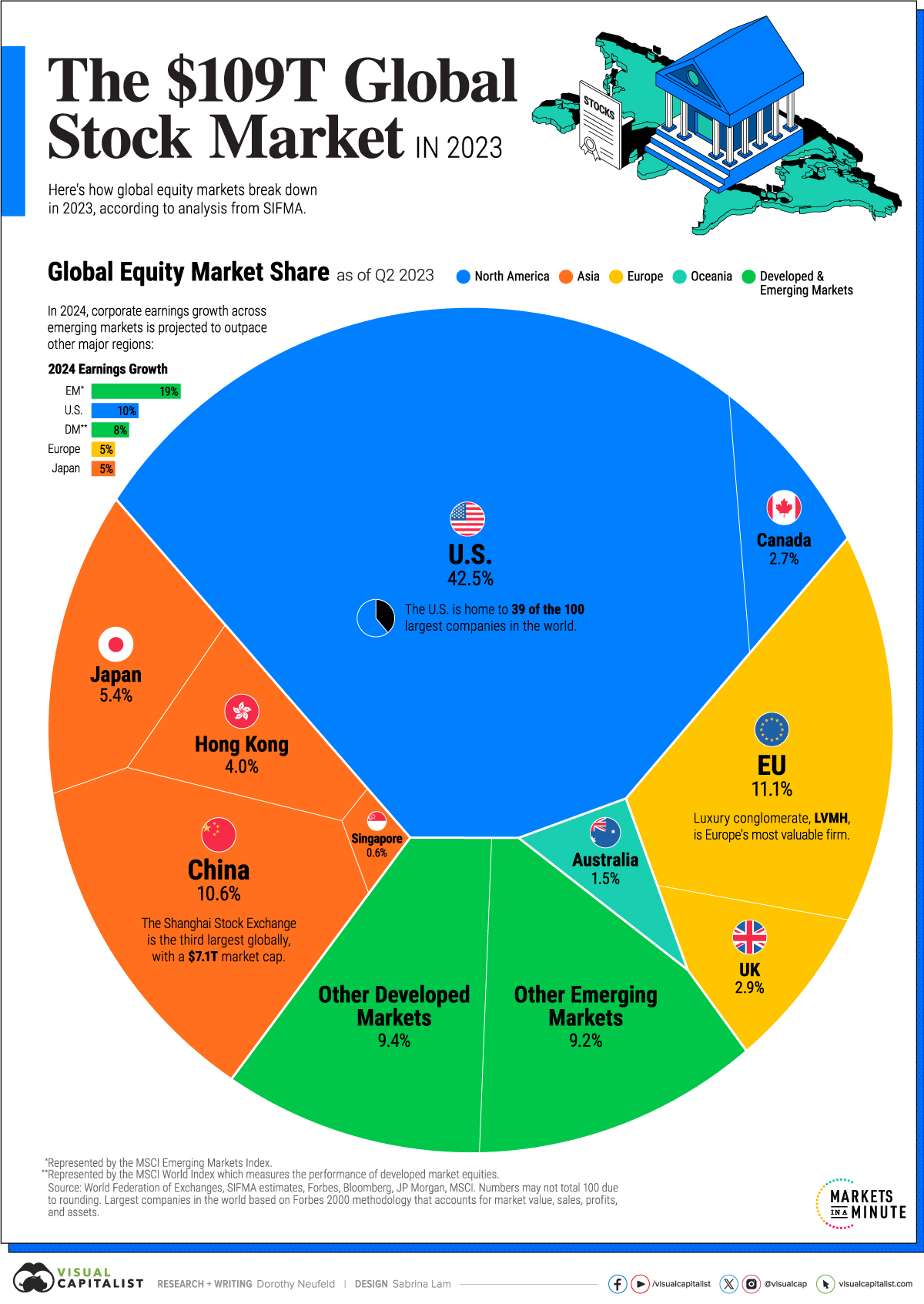 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective For Investors
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective For Investors
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Controversy Erupts Hegseths Signal Chat And Pentagon Accusations
Apr 22, 2025
Controversy Erupts Hegseths Signal Chat And Pentagon Accusations
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The Crucial Role Of Middle Managers In Organizations
Apr 22, 2025
Understanding The Crucial Role Of Middle Managers In Organizations
Apr 22, 2025 -
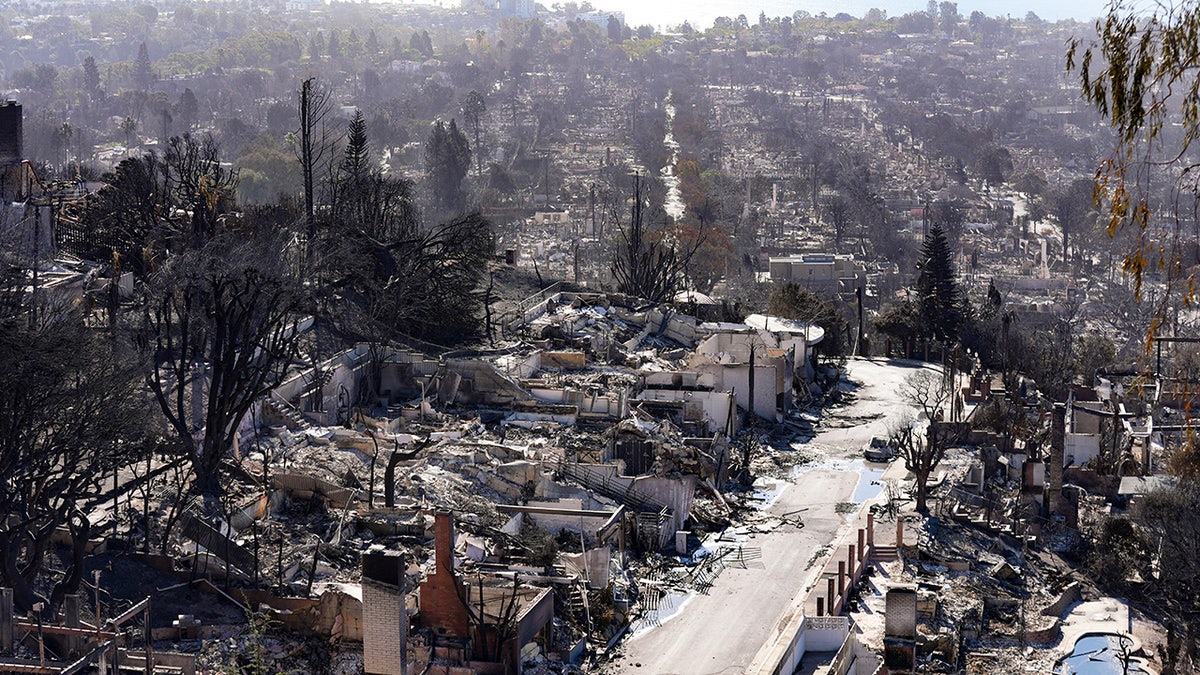 Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting
Apr 22, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting
Apr 22, 2025
