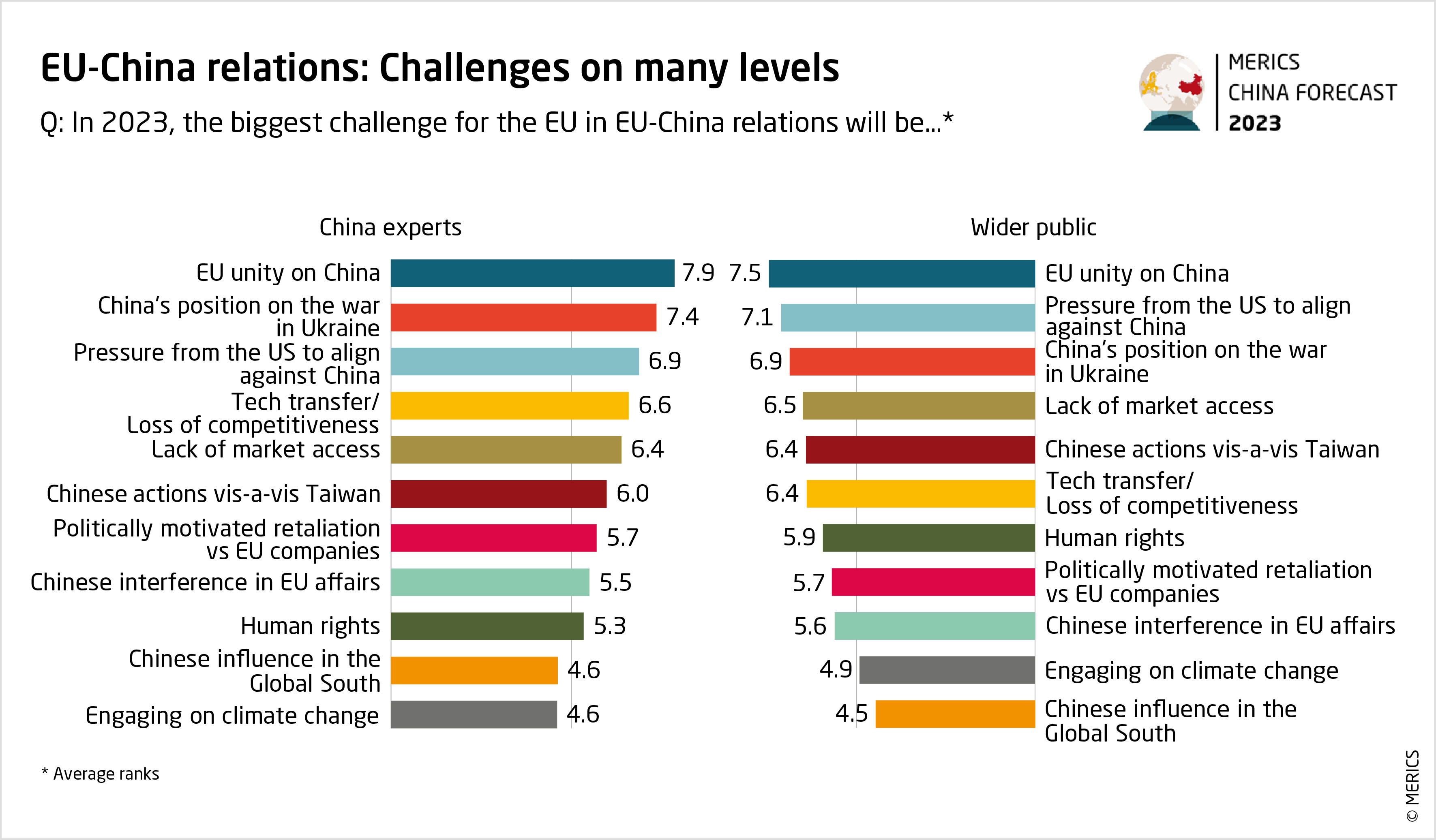
Spot Market Intervention: The EU's Approach To Phasing Out Russian Gas

Table of Contents
The Challenges of Reducing Reliance on Russian Gas
For decades, the EU has been heavily reliant on Russian gas, with Russia historically being a major supplier. This dependence, however, has created significant vulnerabilities. The challenges of reducing this Russian gas dependence are multifaceted and far-reaching:
-
Geopolitical Vulnerability: The reliance on a single, politically unstable supplier exposes the EU to geopolitical pressure and manipulation, as demonstrated by Russia's weaponization of energy supplies. This highlights the urgent need for energy security improvements.
-
Price Volatility: Dependence on a single supplier restricts market competition, leading to price volatility and exposing consumers and businesses to significant price shocks.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The dependence on a single pipeline infrastructure makes the EU vulnerable to supply disruptions caused by geopolitical events, infrastructure failures, or even unforeseen circumstances.
-
Infrastructure Limitations: The EU's energy infrastructure is not fully equipped to handle a rapid shift away from Russian gas, requiring significant investments in diversifying import routes and enhancing storage capacity. This includes upgrading existing infrastructure and building new pipelines for LNG imports.
Spot Market Mechanisms: A Key Tool for Intervention
Spot gas markets are crucial in the current energy crisis. These markets involve the buying and selling of natural gas for immediate or near-term delivery. Unlike long-term contracts, spot market purchases offer significant flexibility, allowing the EU to adjust its gas procurement strategy in response to fluctuating supply and demand.
Spot market mechanisms provide several vital tools for energy trading and gas supply diversification:
-
Auctions and Tenders for Gas Supply: The EU is increasingly using auctions and tenders to procure gas from diverse sources, ensuring competitive pricing and transparency.
-
Increased Collaboration Between Member States: Joint purchasing schemes and coordinated strategies among member states are crucial to increase bargaining power in the global spot gas market.
-
Negotiation of Favorable Supply Contracts with Alternative Suppliers: The EU is actively negotiating contracts with alternative suppliers in regions like Norway, the US, and Qatar, leveraging its collective purchasing power to secure better deals.
EU Strategies for Spot Market Intervention
The EU is implementing several strategies to strengthen its position in spot gas markets and enhance its energy security. The Agency for the Cooperation of Energy Regulators (ACER) plays a vital role in coordinating these efforts through regulatory oversight and market monitoring. Key EU initiatives include:
-
Joint Gas Purchasing Schemes: Collaborative purchasing initiatives allow member states to pool their resources and negotiate more favorable prices and secure larger volumes of gas.
-
Strategic Gas Reserves: The EU is establishing strategic gas reserves to act as a buffer against supply disruptions and price volatility, bolstering gas storage capacity.
-
Support for Renewable Energy Development: Accelerating the transition to renewable energy sources (wind, solar, etc.) reduces overall gas demand and strengthens the EU’s long-term energy independence.
-
Investment in Gas Infrastructure Upgrades: Significant investments are required to improve existing infrastructure, build new LNG terminals, and create alternative import routes, further aiding gas supply diversification.
Successes and Challenges of the EU's Approach
The EU's strategy to reduce its reliance on Russian gas has yielded some successes, including securing alternative gas supplies and bolstering gas storage capacity. However, the transition remains a significant challenge:
-
Price Volatility and Market Manipulation Concerns: The global gas price volatility remains a concern, and the EU needs robust mechanisms to prevent market manipulation and ensure fair pricing.
-
Competition for Limited Global Gas Supplies: The EU is competing with other major gas importers for limited global supplies, creating pressure on prices and requiring further diversification efforts.
-
Potential Need for Further Regulatory Intervention: Further regulatory measures may be needed to streamline the gas market, enhance transparency, and ensure the long-term effectiveness of energy market regulation.
Conclusion
The EU's reliance on Russian gas has created significant vulnerabilities, underscoring the importance of spot market intervention as a crucial tool for achieving energy independence and security. The EU's approach, while showing some success, faces considerable challenges including gas price volatility and competition for global supplies. Further research and discussion on effective strategies for spot market intervention are essential to ensure a secure and sustainable energy future for Europe. Stay informed on developments in the EU’s spot gas market strategy and its implications for energy security.

Featured Posts
-
 Niftys Bull Market A Deep Dive Into The Driving Forces In Indias Market
Apr 24, 2025
Niftys Bull Market A Deep Dive Into The Driving Forces In Indias Market
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 24, 2025
Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare
Apr 24, 2025
Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Wildfire Betting A Reflection Of Our Times Los Angeles Focus
Apr 24, 2025
Wildfire Betting A Reflection Of Our Times Los Angeles Focus
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hopes Shocking Twists Liams Pledge To Steffy And Lunas Impact The Bold And The Beautifuls Upcoming Episodes
Apr 24, 2025
Hopes Shocking Twists Liams Pledge To Steffy And Lunas Impact The Bold And The Beautifuls Upcoming Episodes
Apr 24, 2025
